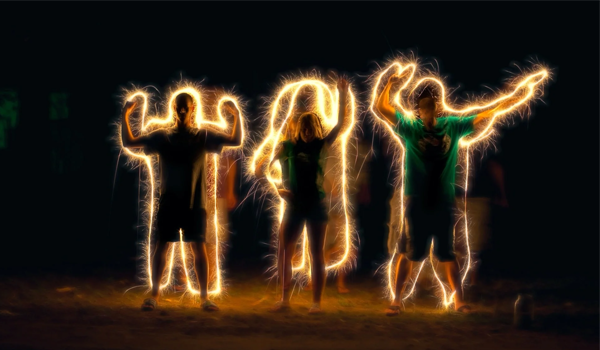Exploring How Light Painting Works in Photography
Light painting is a fascinating and creative technique in photography that combines long exposure times with the movement of light sources to create stunning visual effects. Whether you’re a professional photographer or an enthusiastic amateur, understanding how light painting works can open up new avenues for artistic expression.
Light painting photography involves manipulating light during a long exposure to “paint” in the frame. This can be done by moving the light source or by moving the camera itself. The possibilities are nearly endless, ranging from drawing intricate patterns to highlighting specific parts of a scene. But how does light painting work in practice, and what makes it such a unique art form? Let’s explore this concept further.
What is Light Painting?

Light painting is a technique where photographers use a moving light source to “paint” an image while the camera’s shutter is left open for an extended period. The resulting photographs can range from abstract streaks of light to more detailed, intentional designs that tell a story or highlight a subject in a unique way.
In this technique, the photographer typically works in a dark environment and uses various light sources—such as LED lights, flashlights, or even sparklers—to create light trails. The camera captures these trails as the light moves across the scene, resulting in an image that combines the light patterns with any other elements in the frame.
Defining Light Painting in Photography
Light painting in photography is defined by the use of long exposure settings on a camera to capture the movement of light sources within the frame. This method allows photographers to create images where the light itself becomes a dynamic element, shaping the final photograph in ways that static light cannot achieve.
For light painting to work effectively, the photographer must have precise control over the camera settings, particularly the shutter speed. A slow shutter speed—often several seconds to minutes long—gives the photographer ample time to move the light source through the scene, creating the desired effect. Additionally, tools like tripods are essential to prevent unwanted camera shake, ensuring the only movement in the shot is that of the light source itself.
History and Evolution of Light Painting
The history of light painting dates back to the early 20th century, with the technique evolving alongside advancements in photography. One of the pioneers of light painting was Gjon Mili, a photographer who, in collaboration with Harold Edgerton from MIT, used stroboscopic lights to capture motion in a single frame during the 1930s and 1940s. This early work laid the foundation for modern light painting techniques.
Perhaps the most famous example of light painting is the collaboration between Mili and Pablo Picasso in 1949, where Picasso used a small light to “draw” in the air while Mili captured the movements with his camera. These images, known as Picasso’s “light drawings,” have become iconic representations of the art form.
Over the decades, light painting has continued to evolve, with photographers experimenting with different light sources, techniques, and tools to push the boundaries of this artistic medium. Today, light painting is a widely recognized and practiced form of photography, celebrated for its blend of technical skill and creative expression.
Essential Equipment for Light Painting

To achieve stunning light painting results, having the right equipment is crucial. While creativity and technique play significant roles, the tools you use can dramatically influence the outcome of your light painting photography. From choosing the appropriate camera and lenses to selecting the best light sources, each piece of gear serves a specific purpose that helps bring your vision to life. Additionally, a stable tripod is indispensable for ensuring that your long exposure shots are sharp and clear, allowing the light patterns to stand out without any motion blur from unintended camera movement.
Choosing the Right Camera and Lenses
When it comes to light painting, not just any camera will do. Ideally, you need a camera that allows for manual control over shutter speed, aperture, and ISO settings. DSLR and mirrorless cameras are preferred because they offer the flexibility needed for long exposure photography, which is essential for light painting to work effectively.
A camera with a full-frame sensor is advantageous because it can capture more light and detail, which is particularly useful in low-light conditions where light painting is typically done. The lenses you choose should also allow for manual focus and have a wide aperture (such as f/2.8 or lower) to let in as much light as possible. A wide-angle lens is often preferred for capturing large scenes, while a prime lens can be ideal for more focused, detailed work.
Must-Have Light Sources for Creative Effects
The light sources you use in light painting are just as important as your camera setup. Various tools can be employed to create different effects, and understanding how light painting works with these sources can help you achieve the desired outcome.
- LED Lights: These are versatile and come in various colors and sizes. LED wands and strips are popular for creating sweeping light patterns.
- Flashlights: A basic but effective tool, flashlights can be used to draw or highlight specific areas in your scene. Diffusing the light can also soften its effect.
- Sparklers: These are perfect for creating dramatic, fiery trails and are often used in outdoor light painting.
- Light Brushes: These are specialized tools designed for light painting, offering a range of attachments to create different textures and effects in your photos.
The Importance of a Stable Tripod
A stable tripod is perhaps the most essential piece of equipment for light painting. Since light painting works by using long exposure times, any movement of the camera during the exposure can ruin the shot by introducing unwanted blur. A good tripod ensures that the camera remains completely still, allowing the light trails to appear sharp and defined.
When selecting a tripod, look for one that is sturdy and can handle the weight of your camera setup. Features like adjustable legs, a secure ball head, and even weight hooks (for added stability) can make a significant difference in maintaining camera stability during long exposures. For added security, using a remote shutter release or a timer can prevent camera shake caused by pressing the shutter button.
By equipping yourself with the right gear, you can master the art of light painting and produce images that truly stand out. Each piece of equipment plays a role in how well light painting works, helping you to capture the beauty and complexity of light in motion.
Setting Up Your Camera for Light Painting

To capture the mesmerizing effects of light painting, setting up your camera correctly is essential. The success of your light painting photography hinges not only on the tools you use but also on how well you configure your camera settings. Understanding how to balance shutter speed, ISO, and aperture will significantly influence the quality of your images. Additionally, knowing when to use manual focus over autofocus, especially in low-light conditions, and utilizing the bulb mode for extended exposures are key techniques that can elevate your light painting shots to the next level.
Understanding Shutter Speed, ISO, and Aperture
In light painting, the interplay between shutter speed, ISO, and aperture is crucial. Shutter speed controls the length of time your camera’s sensor is exposed to light. For light painting, slow shutter speeds—typically ranging from 10 seconds to several minutes—allow the camera to capture the full movement of the light source, creating the desired trails and patterns. The slower the shutter speed, the more light the camera captures, which is essential for light painting to work effectively.
ISO settings determine the sensitivity of your camera’s sensor to light. A lower ISO (100-400) is generally recommended to reduce noise and ensure a clean, smooth image, especially when working in dark environments typical of light painting sessions.
Aperture, indicated by f-stops, controls the amount of light entering the camera. A smaller aperture (larger f-number like f/8 or f/16) is often used to increase depth of field and reduce the impact of ambient light, allowing the light trails to stand out more prominently against a darker background.
Manual Focus vs Autofocus in Low Light
Focusing in low light can be challenging, and this is where understanding the difference between manual focus and autofocus becomes important. Autofocus systems may struggle in the dark, leading to blurred images as the camera hunts for something to lock onto. To avoid this, manual focus is typically preferred in light painting. By manually setting your focus point, you ensure that your subject or the area where the light painting will occur remains sharp throughout the exposure.
A useful tip is to pre-focus your lens on a specific point in the scene while there’s still some light available or by using a flashlight to illuminate the focus point temporarily. Once focused, switch the lens to manual mode to lock the focus for the entire session.
Using the Bulb Mode for Extended Exposures
Bulb mode is an essential feature for light painting, as it allows the photographer to control the length of the exposure manually. Unlike standard shutter speed settings, which have a maximum time limit (usually 30 seconds), bulb mode keeps the shutter open for as long as the shutter button is held down. This is particularly useful for light painting scenes that require extended exposure times beyond what your camera typically offers.
When using bulb mode, a remote shutter release is highly recommended to prevent camera shake during the long exposure. This setup ensures that the camera remains stable, capturing every detail of the light movement without any unintended blur.
Setting up your camera with these considerations in mind ensures that light painting works as intended, giving you the control needed to create visually striking images that capture the beauty and complexity of light in motion.
Basic Techniques in Light Painting
Mastering the basics of light painting involves understanding and applying fundamental techniques that form the foundation of this art form. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to refine your skills, focusing on simple yet effective methods is crucial for creating impactful images. Starting with basic strokes, experimenting with different angles and movements, and learning how to manage exposure will help you gain confidence and control in your light painting endeavors. By honing these techniques, you’ll ensure that your work reflects both creativity and technical precision, making the most out of how light painting works.
Simple Strokes: The Foundation of Light Painting

The simplest approach to light painting involves creating basic strokes with your light source. These strokes are the building blocks of more complex designs and patterns. To start, choose a light source such as a flashlight or an LED wand. With your camera set to a long exposure, move the light source in steady, deliberate motions to create lines, shapes, or even letters in the air.
For beginners, practicing straight lines, circles, and basic shapes helps build an understanding of how the light interacts with the camera’s sensor over time. These fundamental movements allow you to see the immediate effects of your actions, providing insight into how light painting works and how different speeds and distances from the camera affect the final image.
Experimenting with Different Angles and Movements
Once you’ve mastered the basics, experimenting with angles and movements can add depth and dimension to your light paintings. Changing the angle of your light source relative to the camera can create varying effects, from soft, diffused glows to sharp, intense lines. Try moving the light source closer or further from the camera to see how the light trails change in thickness and intensity.
You can also incorporate more dynamic movements, such as spirals, zigzags, or waves, to bring energy and flow to your compositions. Rotating the camera itself during the exposure, a technique known as camera rotation, can produce intriguing abstract patterns that further explore the potential of light painting.
How to Avoid Overexposure and Hot Spots
One of the challenges in light painting is managing exposure to avoid overexposed areas, known as “hot spots,” where the light is too intense and details are lost. Overexposure occurs when the light source is too bright, too close to the camera, or held in one spot for too long. To prevent this, consider the following techniques:
- Adjust the Light Source: Use dimmer lights or diffuse your light source with a filter to reduce its intensity.
- Move the Light Quickly: Keep the light moving to avoid concentrated brightness in one area.
- Control the Exposure Settings: Lower the ISO and use a smaller aperture to limit the amount of light hitting the sensor. These adjustments can help maintain detail and texture in your light painting.
By paying attention to these details, you can create balanced light paintings where the light trails enhance the image without overpowering it, demonstrating a thorough understanding of how light painting works in practice.
Advanced Light Painting Techniques
Once you’ve mastered the basics of light painting, exploring advanced techniques can take your creative photography to the next level. These techniques allow you to push the boundaries of what can be achieved with light and long exposure, adding complexity and depth to your images. From creating dramatic silhouettes and intricate light trails to using multiple light sources and reflective surfaces, these methods offer endless possibilities for artistic expression. Understanding how light painting works at an advanced level will help you craft images that are not only visually stunning but also rich in detail and creativity.
Creating Silhouettes and Light Trails
One of the most effective advanced techniques in light painting is combining silhouettes with light trails. This method involves placing a subject—such as a person or object—between the camera and the light source. The subject blocks the light, creating a dark outline or silhouette against the vibrant trails of light that surround them. This contrast can add drama and focus to your image, making the silhouette the centerpiece while the light trails enhance the overall composition.
To achieve this effect, position your subject close to the camera and light the background with your chosen light source. As you move the light behind the subject, be careful to avoid directly illuminating them to maintain the silhouette. Experimenting with different angles and movements can create a variety of shapes and patterns, highlighting how light painting works in creating both static and dynamic elements within the same frame.
Using Multiple Light Sources for Complex Designs
Incorporating multiple light sources into your light painting allows for more intricate and layered designs. Each light source can be used to create different colors, textures, and patterns within the same image. For instance, you can use a combination of LED wands, flashlights, and even lasers to produce overlapping light trails that interact with each other in complex ways.
This technique requires careful planning and control over each light source’s movement and timing. It’s essential to practice with each light source individually before combining them, to understand how they affect the exposure and composition. By layering different light effects, you can create images that are rich in detail and visually compelling, demonstrating a deep understanding of how light painting works in more sophisticated scenarios.
Integrating Reflective Surfaces for Dynamic Effects
Using reflective surfaces in light painting can add a dynamic and surreal quality to your images. Mirrors, glass, water, and metallic objects can reflect and scatter light in unexpected ways, creating additional light trails, doubling patterns, or introducing new textures into your composition.
To use this technique, position the reflective surface within your scene where it can catch and reflect the light source. For example, placing a mirror in the foreground can reflect light trails from behind, creating the illusion of additional light sources. Adjusting the angle of the reflective surface allows you to control the direction and intensity of the reflections, adding another layer of complexity to your light painting.
This technique not only enhances the visual appeal of your work but also challenges your understanding of how light painting works with different materials, leading to more innovative and creative outcomes.
Conclusion
Light painting is a versatile and captivating technique that allows photographers to blend creativity with technical precision. Whether you’re creating simple light trails or experimenting with complex designs, understanding how light painting works can open up a world of artistic possibilities. By mastering the fundamentals and exploring advanced techniques, you can push the boundaries of your photography and create images that are not only visually stunning but also deeply engaging.
As you continue to practice and refine your skills, remember that light painting is as much about experimentation as it is about precision. Every new tool, angle, and setting can lead to unexpected and exciting results, making the journey of learning how light painting works a truly rewarding experience. With patience and creativity, you can develop a unique style that reflects your artistic vision and passion for light painting.